What the system is comprised of and what it does
1. What is the cardiovascular system comprised of and what are the three types of blood vessel?
Answer: heart and blood vessels; arteries and veins.
The heart
2. Describe the heart.
Answer: A fist sized, muscular organ located in the thorax.
The blood
3. In addition to oxygen name four things that the blood transports.
Answer: nutrients, hormones, waste products, heat.
The heart
4. What are the four chambers of the heart?
Answer: atria (right and left); ventricles (right and left).
The blood vessels attached to the heart
5. What are the four blood vessels attached to the heart?
Answer: aorta; venae cavae; pulmonary vein; pulmonary arteries.
The heart valves
6. What are the four valves in the heart?
Answer: aortic valve; pulmonary valve; tricuspid valve; mitral valve.
The blood vessels attached to the heart
7. Which blood vessels attached to the heart carry oxygenated blood and deoxygented blood, respectively?
The flow of blood in the heart
8. Describe the flow of blood through the heart.
Answer: (starting at venae cavae) right atrium to right ventricle; pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein; left atrium to left ventricle; aorta.
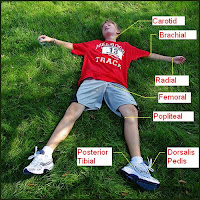
Pulses
9. In addition to the radial pulse, name 8 other sites on the body where a pulse can be felt (0.5 marks each).
Answer: temporal; facial; carotid; brachial; femoral; polliteal; posterior tibial; doralis pedis.
Electrical activity in the heart
10. Describe the generation and spead of electrical activity in the heart.
Answer: generated at the sinoatrial node; travels to atrioventricual node and spreads across atria; travels through septum along Purkinje fibres; spreads across ventricles.
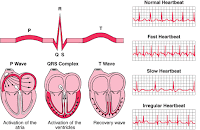
11. What is a trace of electrical activity in the heart called: what are the three sets of patterns observed?
Answer: an electrocardiogram; P-wave; QRS-complex; T-wave.
12. What is happening at the three wave patterns on the electrocardiogram? What can happen to the T-wave in a myocardial infarction?
Answer: atrial depolarisation; ventricular depolarisation; ventricular repolarisation; it is elevated.
Cardiac cycle
13. What are the two stages of the cardiac cycle and what is happening at each stage?
Answer: diastole and systole; heart relaxes and contracts, respectively.
Cardiac output
14. Describe the cardiac output; what are its components and how is it calculated?
Answer: the blood pumped by the heart in one minute; stroke volume and heart rate; CO=HR x SV.
15. What effect do: sympathetic stimulation, parasympathetic stimulation and increased end diastolic volume have, respectively, on the cardiac output? What happens to resting heart rate in athletes?
Answer: increases; decreases; increases; decreases.
Blood vessels
16. What type of muscle is found in arteries and veins? How does this differ between arteries and veins? What do veins have that arteries lack? What is the space in the middle of a blood vessel called?
Answer: smooth muscle; thicker in arteries; valves; lumen.
Blood pressure
17. What are the two factors that determine blood pressure? What is the equation for bood pressuer based on these factors (2 marks)?
Answer: cardiac output and peripheral resistance; BP = CO x PR.
Capillary exchange
18. What two factors determine capillary exchange? Which is larger at the arterial end of the capillary bed; what is the fluid in the tissues called?
Answer: blood pressure and osmotic pressure; blood pressure; interstitial fluid.
Control of blood pressure
19. How are the medulla and the kidneys, respectively, involved in control of blood pressure?
Answer: medulla - heart rate and peripheral resistance; kidneys - blood volume and peripheral resistance.
Blood
20. What are the three formed elements in the blood? How is one of these formed elements further subdivided into two main types?
Answer: erythrocytes, leucocytes, platelets. Leucocytes subdivided into granulocytes and agranulocytes.
21. Describe four unique things about the specialisation of the erythrocyte.
Answer: Shape; no nucleus; no mitochondria; full of haemoglobin.
22. What are the four main blood types?
Answer: A; B; O; AB.




















No comments:
Post a Comment